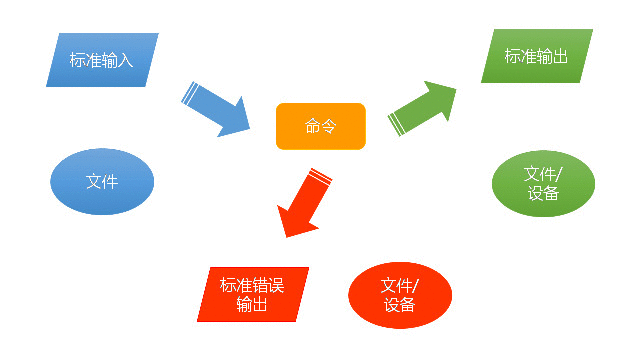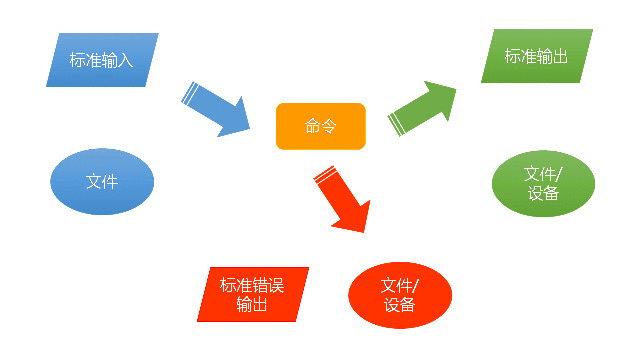
输入输出重定向,又称数据流重定向,指的是将标准输出、标准错误输出或标准输入重新定向,输出到文件或从文件输入。下图是命令的数据流示意图:
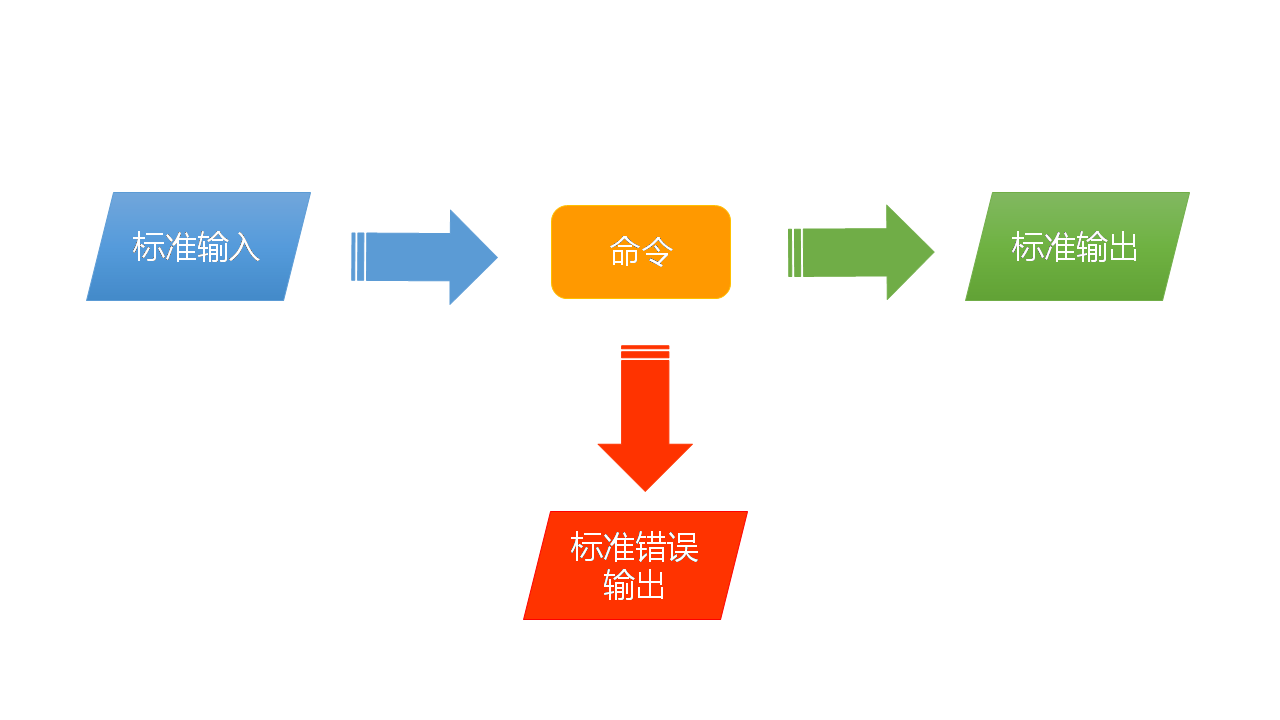
输入输出重定向共有3类6种情况:
输入输出类型 文件描述符 对应的重定向 符号
标准输入 0 标准输入重定向 <
即时输入重定向 <<
标准输出 1 标准输出重定向 > 或 1>
标准输出添加重定向 >> 或 1>>
标准错误输出 2 标准错误输出重定向 2>
标准错误输出添加重定向 2>>
Linux给每个打开的文件赋予一个非负整数作为其文件描述符,用户可以直接使用描述符引用对应的文件。系统为每个进程自动打开3个标准文件(标准输入、标准输出和标准错误输出),其文件描述符分别为0、1和2。
下面,我们分别学习这几类重定向及其用法。
1. 标准输出重定向
Shell命令默认的输出一般都是标准输出(通常是屏幕),我们可以利用输出重定向命令,将输出写入到文件,如下图所示:
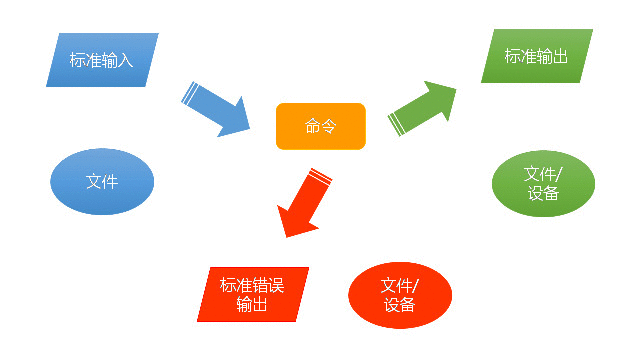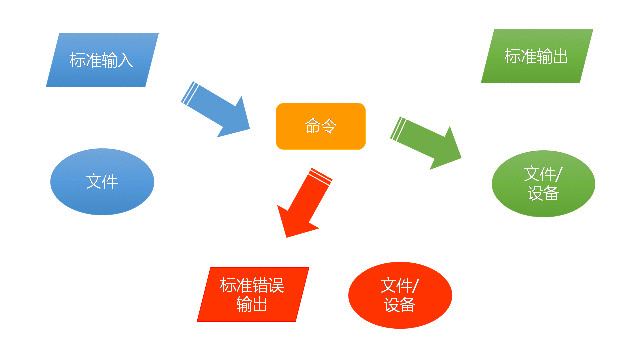
输出重定向是最常用的一种重定向。如果重定向的文件不存在,则会新建一个文件。但如果文件已经存在,使用重定向">",会覆盖原文件的内容;而用添加重定向">>",则是添加到文件原内容的后面。
[peter@ibi-genome redirection]$ whoami #whoami命令结果输出到屏幕(标准输出) peter [peter@ibi-genome redirection]$ ls hello.sh [peter@ibi-genome redirection]$ whoami >user #屏幕上没有输出了 [peter@ibi-genome redirection]$ ls #当前目录下多了user文件 hello.sh user [peter@ibi-genome redirection]$ cat user #whoami命令的输出写入文件user中了 peter [peter@ibi-genome redirection]$ date >user [peter@ibi-genome redirection]$ cat user #文件user原来的内容被覆盖 2017年 04月 30日 星期日 08:58:59 CST [peter@ibi-genome redirection]$ whoami >>user [peter@ibi-genome redirection]$ cat user #新内容添加到文件user原内容的后面 2017年 04月 30日 星期日 08:58:59 CST peter
2. 标准错误输出重定向
Shell命令如果正确执行了,就没有提示(如rm命令)或显示执行结果(如ls命令)。如果命令执行出错,则会在屏幕上显示错误提示,也就是标准错误输出。标准错误输出也可以重定向到文件中,即标准错误输出重定向。
与标准输出一样,Linux的标准错误输出也是显示到屏幕上,所以很容易与标准输出混淆。
[peter@ibi-genome ~]$ ls hello.sh user [peter@ibi-genome ~]$ cat hello.sh #!/bin/bash echo "Hello world!" [peter@ibi-genome ~]$ cat hello.pl #当前目录下并没有hello.pl文件 cat: hello.pl: 没有那个文件或目录 #命令出错提示,即标准错误输出 [peter@ibi-genome ~]$ cat hello.sh >file_sh [peter@ibi-genome ~]$ cat hello.pl >file_pl #用标准输出重定向,屏幕上仍然显示错误信息 cat: hello.pl: 没有那个文件或目录 [peter@ibi-genome ~]$ cat file_sh #!/bin/bash echo "Hello world!" [peter@ibi-genome ~]$ cat file_pl #该文件是空的 [peter@ibi-genome ~]$ cat hello.pl 2>file_pl #使用错误输出重定向,屏幕上不再有错误提示 [peter@ibi-genome ~]$ cat file_pl #上面的错误提示写到了文件file_pl中 cat: hello.pl: 没有那个文件或目录
错误输出重定向的写法是2>file,因为我们前面已经知道,标准错误输出的文件描述符是2。其实,上面的标准输出重定向完整的写法应该是1>file,一般把文件描述符1省略。与">>file"类似,如果后面的文件已存在,"2>>file"可将标准错误输出添加到文件原内容的后面。
输出重定向和错误输出重定向后面的文件,可以是普通文件,也可以是设备文件或管道文件。Linux有一个特殊的设备文件/dev/null,该文件就像一个黑洞,所有东西进去就再也找不到了。如果您觉得一个命令的输出或错误提示太烦了,就可以把他们定向到该文件,整个世界马上就清静了。
[peter@ibi-genome redirection]$ ls >/dev/null [peter@ibi-genome redirection]$ cat hello.pl 2>/dev/null
一个命令可以同时使用输出重定向和错误输出重定向:
[peter@ibi-genome redirection]$ cat hello.sh hello.pl >file_sh 2>file_err
标准输出也可以和标准错误输出合并后重定向到同一个文件:
[peter@ibi-genome redirection]$ cat hello.sh hello.pl >file 2>&1 [peter@ibi-genome redirection]$ cat file #!/bin/bash echo "Hello world!" cat: hello.pl: 没有那个文件或目录
3. 标准输入重定向
标准输入重定向指把命令的数据来源从标准输入(一般指键盘)重定向为从文件读取。
有些命令只能从标准输入读取数据,如tr命令。我们可以利用输入重定向使其从文件读取数据:
[peter@ibi-genome redirection]$ cat hello.sh #!/bin/bash echo "Hello world!" [peter@ibi-genome redirection]$ cat hello.sh |tr b B #!/Bin/Bash echo "Hello world!" [peter@ibi-genome redirection]$ tr b B <hello.sh #!/Bin/Bash echo "Hello world!"
另外,如果我们想往一个文件写入几行文字,可以用即时输入重定向(<<):
[peter@ibi-genome redirection]$ cat >hello.pl <<eof > #!/usr/bin/perl > print "Hello world\n"; > eof [peter@ibi-genome redirection]$ cat hello.pl #!/usr/bin/perl print "Hello world\n";
其中的eof是输入结束的标志,可以使用别的字符串,但建议用不常见的,因为如果使用常用的字符串,碰巧您输入的内容里有该字符串,就会提前结束输入。
输入输出重定向是Shell重要的概念,要在理解的基础上多加以应用才能较好地掌握。